| Product introduction |
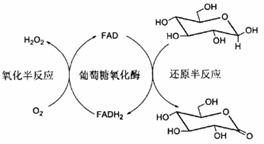
A glucose oxide can generate glucose acid REDOX enzyme. This enzyme for beta-D-glucose showed high specificity. This enzyme to flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) as a coenzyme, each molecule contains two FAD. Exist such enzymes in the honey. Many of these microorganisms, especially mould can produce the enzyme. Common Aspergillus, penicillium and other production. Molecular weight: 160 kDa (gel filtration) isoelectric point PI: extinction coefficient 4.2:E1% = 16.7(280 nm) from Aspergillus Niger, Aspergillus Niger) separation of glucose oxidase is a dimer, consists of two equal to the base unit, each of the Molecular weight of 80 kDa. Each sub unit contains a flavin adenine dinucleotide part and an iron. This enzyme is a kind of glycoprotein, contain? 16% of Neutral sugar and 2% of amino sugar. The enzyme also contains three cysteine residues and eight potential glycosylation sites N-connection. Glucose oxidase is the ability to oxidation at different rates of single DNA-D-Glucose, D-aldose and methyl-D-Glucose. Glucose oxidase optimum pH 5.5, at the same time it has a wide pH range activity for 4-7. Glucose oxidase specific scope beta-D-Glucose (KM33-110-mM). The Glucose oxidase don't require any activation factor, but it can be Ag+, Hg2+, Cu2+, mercury benzene acetic acid and P-chloromercuribenzoate inhibition. It will not be non-metallic SH reagents inhibiting: such as N-ethyl maleic imide, indole acetic acid, iodine acetamide. Glucose oxidase is also used in enzymatic determination of d-glucose in the solution. Because of Glucose oxidase beta-D-Glucose oxidation, making it a D-gluconolactate and hydrogen peroxide, horseradish peroxidase enzyme used in the determination of Glucose is often used as matching. |